Morphology of flowering plants 1!
Angiosperms show a large diversity in external structure or morphology. The presence of roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and fruits is the characteristic feature of angiosperms.
The underground part is the root system which is developed from the radicle and the portion above the ground forms the shoot system which is formed from plumule.
Types of roots:
- Tap roots: It is mainly seen in dicot plants. It is the direct elongation of the radicle which leads to the formation of primary roots. Eg. Mustard plant.
- Adventitious roots: Roots develop from parts of the plant other than the radicle. Eg. Grass, Monstera, and Banyan tree, etc.
- Fibrous roots: Mainly seen in monocot plants. Here primary root is short-lived and is replaced by a large number of roots. Eg. Wheat plant.
NOTE: Fibrous roots originate from the base of the stem. Whereas primary roots and their branches constitute the tap root system.
Functions of roots:
- Proper anchorage.
- Absorption.
- Storage.
- Synthesis of plant growth hormone.
MODIFICATIONS OF TAP ROOTS:
Fusiform/spindle roots | Radish |
Conical roots | Carrot |
Napiform | Beetroot |
Pneumatophores | Rhizophora (Mangrove plant) |

MODIFICATIONS OF ADVENTITIOUS ROOTS
Fasciculated roots | Asparagus, Dahlia |
Tuberous adventitious roots | Sweet potato(Ipomoea batatas) |
Stilt roots/brace roots | Maize, sugarcane |
Prop/pillar roots | Banyan (Ficus benghalensis) |
Climbing roots | Money plant(Pothos), Monstera |
Foliar/ Epiphyllous roots | Bryophyllum |
Sucking/Haustorial/Parasitic roots | Cuscuta |
Stem:
It is the aerial part of the plant. It is positively phototropic, negatively hydrotropic, and negatively geotropic. Nodes and internodes are the distinguishing features between roots and stem.
MODIFICATION OF STEM:

UNDERGROUND STEM | SUB-AERIAL STEM | AERIAL STEM |
Rhizome- eg. Ginger and turmeric. | Runner- eg. Grass, Oxalis, Common strawberry. | Stem tendril- eg. Cucurbitaceae family. |
Bulb- eg. Garlic and onion. | Stolon- eg. Jasmine, peppermint, Wild strawberry. | Stem thorn- eg. Bougainvillea, Citrus. |
Corm- eg. Amorphophallus/Elephant foot/ Suran. | Sucker- eg. Banana, Mint, Pineapple, Chrysanthemum. | Phylloclade- eg. Opuntia (flat) and Euphorbia (cylindrical) |
Tuber- eg. Potato. | Offset- eg. Pistia and Eichornia. | Cladode- eg. Asparagus, Ruscus. |
LEAF:
Leaf develops from nodes and performs the function of photosynthesis. It shows lateral growth. They are arranged in acropetal order.
Note: In monocots sometimes the leaf base (hypo podium) forms a sheath covering that is partially wholly and in members of the Fabaceae family the leaf base is swollen which is called a pulvinus.
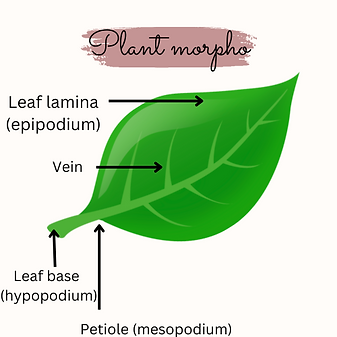
If the pedicel is present then it is called a pedicellate leaf but if the pedicel is absent then it is called a sessile leaf.
If the stipule is present then it is called a stipulate. Eg. the Fabaceae family
But if stipules are not present then it is called an ex-stipulate. Eg. Solanaceae
Stipule type: 1. Tendrilar stipule- eg. Smilax.
2. Foliaceous stipule- eg. Pea.
TYPES OF VENATION:
RETICULATE | PARALLEL |
All dicots. | All monocots. |
Exception- Calophyllum (parallel seen) | Exception- Smilax (Reticulate seen) |
Unicostate- Mango | Unicostate- Banana |
Multicostate- China rose | Multicostate- Fan palm and wheat |
PHYLLOTAXY:
Alternate | Opposite | Whorled |
Leaves are arranged in alternate order. | Leaves are arranged in an opposite manner. | Each node contains more than two leaves and forms whorls. |
Eg. Mustard, China rose, Sunflower. | Eg. Ocimum (Tulsi), Calotropis, and Guava. | Eg. Alstonia, Nerium. |
TYPES OF LEAVES:
- Simple leaf: Eg. Peepal, mango, radish.
- Compound leaf: Compound leaf has two types:
A. Pinnately compound leaf: 1. Incised up to midrib.
2. Midrib is called the rachis.
3. Eg. Neem.
B. Palmately compound leaf: 1. A leaflet is attached at the common point.
2. Rachis is absent.
3. Eg. Silk cotton, Oxalis.

MODIFICATIONS OF LEAVES:
- Leaf Tendril: Tendril helps in climbing. Eg. Pea (Lathyrus aphaca)
- Leaf spine: Pointed spines seen. Eg. Opuntia, Cacti.
- Leaf bladder: Bladder-like structure is observed. Eg. Utricularia (Bladderwort)
- Phyllode: Petiole becomes flat leaf-like green. Eg. Australian acaciasia.
- Fleshy leaves: Eg. Onion and garlic.


